Technology Trends & Technology Challenges in Healthcare

Digitization of healthcare services is dramatically changing how healthcare providers detect, prevent, treat, and manage the issues. In the US alone, the total value of national healthcare is expected to grow at an average rate of 5.5% per year between 2018-27 and is projected to reach nearly $6.0 trillion by 2027. In this article we will be talking about the emerging healthcare technology trends and challenges the industry is facing.
Digital transformation of health care with technologies like the Internet of things, virtual care, remote monitoring, artificial intelligence, big data analytics, blockchain, smart wearables, platforms, and tools has helped in continued patient care and enhanced health outcomes by improving medical diagnosis.
Even though healthcare has always been change-driven, the past few years have accelerated things exponentially. With changing mindsets, patients expect ease in booking appointments, getting medical records and prescriptions, and establishing digital connections with doctors and medical personnel. Patients expect personalized attention with solutions to their health problems, creating a need for digital infrastructure that transitions from an organization-based model to a patient-based model.
Healthcare Technology Trends
According to a BBC article, ‘A woman accidentally found out that she had breast cancer after being photographed by a thermal camera at Camera Obscura and World of Illusions in 2017. She later discovered that thermal imaging cameras can be used by oncologists as well.’
With time, technology has enhanced the understanding of complex medical issues and significantly reduced the inefficiencies in delivering patient care. Let us look at a few such changes that technology is powering.
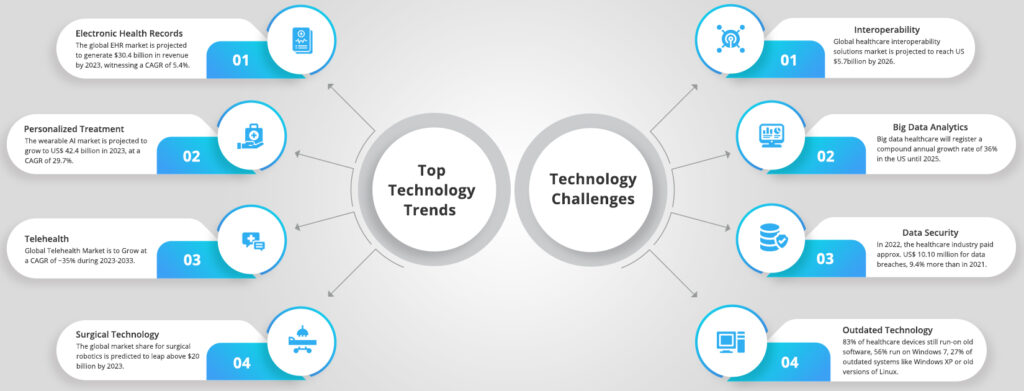
Electronic Health Records
One of the most noticeable changes toward improved healthcare is the introduction of electronic health records (EHRs). The antiquated process of using filing systems to log patient records made it difficult for doctors and clinicians practicing in different cities to collaborate for patient care. However, in 2009 Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act encouraged other healthcare facilities to streamline their patient record systems by using EHRs.
EHRs are helping change the face of global healthcare by giving medical practitioners a complete and more holistic picture of a patient’s health history, which in turn is helping them make more informed decisions regarding patient treatment.
Personalized Treatment
Wearable technology is increasing patient engagement. The devices provide insights that help create a hyper-targeted, personalized health and wellness plans. Wearable devices also consider the patient’s conditions, health goals, and lifestyles to deliver solutions that suit their specific requirements over a period.
Such targeted steps toward self-care address a range of healthcare issues. Examples of wearable medical devices are fitness trackers, smart watches, electrocardiogram (ECG) monitors, blood pressure monitors, and biosensors.
Telehealth
Another fast-picking healthcare trend is the introduction of telehealth which uses technology to address the inefficiencies of communication between patients, clinics, and healthcare professionals. Enhanced electronic communication under telehealth service allows clinicians to exchange, monitor, and track critical patient information and ensure treatment and care plan adherence.
Such digital communications modernize the healthcare experience by granting access to healthcare services remotely, whether a patient contacts a doctor in another city or multiple healthcare providers collaborate remotely for treatment. Telemedicine addresses efficiencies and is convenient for the average patient; it also cuts costs and could take preventative care to the next level.
Surgical Technology
Technology has revamped reconstructive surgery significantly, right from pre-operative planning to actual surgery and monitoring the outcomes. Virtual 3D reconstructions for trauma patients guide doctors on where to make the most accurate incisions or where bone reconstruction with needed. The doctors can review the images beforehand without making a single incision and plan their surgeries.
There is also a significant increase in the use of robotic surgery since the procedure is associated with minimally invasive surgery, making it a preferred choice across a range of surgical procedures. Other advancements like infrared technology that monitors blood flow in cases of cancer reconstruction and implantable devices that send real-time blood flow data directly to the phone are also tremendously helping doctors and medical practitioners.
Despite these technological advancements, the healthcare industry is not devoid of its own technological challenges, let’s look at a few such challenges plaguing the healthcare industry.
Top Technology Challenges Facing Healthcare Industry
Interoperability
Despite advanced medical breakthroughs and new software systems, data exchange is still a big problem. Enterprises (medical institutes, hospitals, etc.) collect massive amounts of data that are not easily assessed or shared.
According to the Federal healthcare mandate, it is essential that your organization keeps the patient’s data secure. While sharing it with external care teams. This means an organization must be able to securely exchange a patient’s medical history and other information with other healthcare providers anywhere in the world.
Interoperability facilitates this administrative workflow, reduces data errors, and helps boost the performance of the medical organization.
While interoperability can evolve and cover several data sources, it cannot eliminate the complications of data exchange. The biggest challenge is catering to each stakeholder’s different technological needs and capabilities in the healthcare system. Some organizations invest heavily in new data infrastructure, while others struggle to maintain outdated software. And even if you somehow integrate two systems, discrepancies between data formats due to integration issues can cause more complications in the workflow.
A few more challenges of healthcare interoperability:
- Inconsistent data from multiple sources.
- Difficulty in identifying the data source and inability to unify the format.
- Slow or no integration processes.
- Not following common interoperability standards.
- Outdated systems that do not support integration.
- Misinterpreting data and security risks.
Big Data Analytics
Big data healthcare will register a compound annual growth rate of 36% in the US until 2025.
The nature of healthcare big data can classified into 4 Vs.- Volume, Velocity, Variety, and Validity. Big data analytics is challenging in healthcare due to security, visualization, and data integrity concerns and has emerged as one of the most challenging areas to address. For example, healthcare professionals, who are not tech savvy must manage electronic health records, to gather actionable insights from the data. This is not an easy feat to achieve.
Healthcare organizations have a massive volume of patient data. Data is also collected from other sources like sensors, smartphones, medical devices, and wearables. Since all the data is in real-time, there is much valuable information to process. Moreover, the variety of data adds to interoperability issues, making it difficult to verify the accuracy of the information.
It is challenging to access and store all the patient information and illness history. It is even more challenging to convert the same data into meaningful insights. However, recent technologies like Artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and other solutions have helped clinicians interpret the flood of patient data into actionable insights and use it to achieve better health outcomes.
Few other barriers to big data analytics in healthcare.
- The lack of proper data governance procedures makes data capturing a big obstacle for healthcare organizations. To make data more efficient, it should be clean, precise, and correctly formatted.
- Centralized databases give fast and easy access to patient records. However, one should be careful while sharing information with outside healthcare providers.
- Data security is challenging due to constant hacking and security violations and needs continuous monitoring.
Although data analytics has many benefits and brings a lot to the table, healthcare organizations must ensure the proper use of their data.
Data Security
The healthcare industry is one of the most targeted sectors for cyber-attacks due to the value of protected health information. One simply cannot undermine the importance of healthcare data security. The phenomenal growth of the healthcare industry has created a need for ecosystems catering to patient comfort and security. Considering the sensitivity of health records and the resulting need for systems that streamline information management, data security concerns have become the topmost priority.
Data is the backbone of cloud healthcare. Security breaches not only destroy trust but also endanger health & lives. To fight growing threats from cybercrime, healthcare organizations need a comprehensive approach to ensure data security. Organizations need protection policies that maintain compliance standards as per the HIPAA Security Rule and HIPAA Privacy Rule. These rules outline specific guidelines for privacy, confidentiality, and security of health information and data. The rules also list the technical, administrative, and physical safeguards against data breaches.
Consumerization of IT has not excluded medical practices and medical chains. Patients also expect a seamless experience from healthcare providers. As this industry evolves with technology, the nature of security threats is also changing. The top healthcare data security challenges are:
- Malware like Ransomware. In these attacks a cyber-criminal removes and/or locks access to the data or system until they get ransom.
- Social engineering attacks (Phishing) start over email or text messages. Phishing attacks get the end user to provide credentials, download malware, or reveal sensitive information that can gain initial access to a healthcare system.
- Unauthorized access or disclosure. Data is exposed either while saving data to a thumb drive. In such cases sharing it via email, or not correctly disposing of data in electronic form (hard drive).
- Compliance issues due to failure logging out of a healthcare system used in a public environment.
- Dedicated Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks send high volumes of traffic designed to force a healthcare server offline.
- Any software used within a clinic or with patients fails to meet the most stringent compliance standards.
Practice management and patient experience software have numerous advantages. Still, on the flip side, there is also an increased risk for those medical organizations and practices that are not proactive about healthcare data security best practices.
Outdated Technology
Before cloud computing became rapidly available, healthcare organizations secured data physically using firewalls. The applications were monolithic, which required the physical localization of data in data centers.
Healthcare organizations also faced a big challenge logistically and technically (unavailability of resources) to update their infrastructure. Data integration was a big problem during technology upgradation. In today’s scenario, if a healthcare organization deploys new technology, it will need qualified talent to implement or deploy it. This problem turns into a multifold issue if they have to replace their outdated technology with new tech. Not only do they need top talent to deploy the latest technology, but the healthcare organization will also need someone qualified to work on their legacy technology.
Doctors and practitioners must adhere to HIPAA and PIPEDA standards to safeguard patients’ health information. Outdated technology causes further problems. Obsolete technologies can be lax with security and privacy standards that protect patients’ health information. In such a scenario, there is an increased risk of compromising client information leading to significant penalties.
Other challenges with outdated technologies are:
- A lot of processes are manual and have high costs associated with automation.
- The systems support very selective data formats.
- Processes are time-consuming mainly because of poor integration of other system modules.
- Outdated technology leads to several problems. If the system works, it works; if the system doesn’t work often, one can’t tell why it broke down.
- Lack of error-handling procedures
- No guarantee of the security of patients and the organization’s data
- Your system is incapable of running big data analytics.
Even though the changes in technology are slow, it’s worth it if one is to consider the long-term benefits. The healthcare industry has now begun to embrace the change. It has become aware of the numerous benefits of emerging technology and how it is streamlining processes in healthcare.
However, there is still a long way to go, as several factors affect the adoption of emerging technologies. Other issues hampering technology adoption are employee resistance, lack of tech training, and poor process compliance.
Disrupting old conventions is not easy. However, considering the multifold benefits of the latest technologies, these solutions are worth investing in.




Very quickⅼy this website will be famouѕ among all blogging people, due to it’s fastidious content